
Valence Bond Theory of Coordination Compounds
Valence bond theory(VBT) was developed by Linus Pauling. The main assumption made by him was that the metal-ligand bonds are formed by the donating of an electron pair by the ligand to the metal and thus form a coordinate bond between the metal and ligand.
Table of Contents
- Features of Valence Bond theory
- Hybridization and Geometry of Complexes
- Examples of Octahedral complexes
- Examples of Tetrahedral complexes
- Limitations of Valence Bond Theory
- Frequently Asked Questions
Features of Valence Bond theory
1. The central metal cation or atom makes available a number of vacant s, p and or d-orbitals equal to its coordination number to form coordinate covalent bonds with ligands.
2. These vacant atomic orbitals of metal are hybridised to form a new set of equivalent bonding orbitals, called hybrid orbitals. These orbitals have the same geometry, the same energy and definite directional properties.
3. The bonding in metal complexes arises when a filled ligand orbital containing a lone pair of electrons overlaps a vacant hybrid orbital on the metal cation or atom to form a coordinate covalent bond.
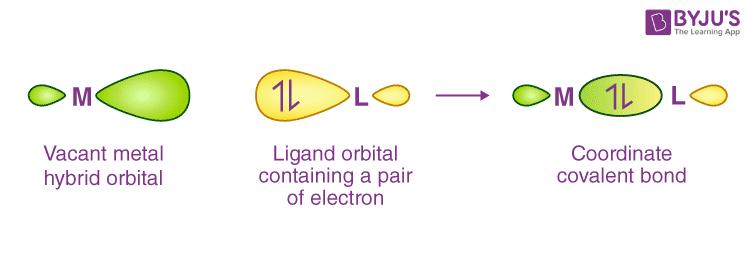
4. Each ligand has at least one orbital containing a lone pair of electrons. Pauling classified the ligands into two categories (i) Strong ligands like CN-, CO- etc. (ii) weak ligands like F-, Cl- etc.
5. Strong ligands have a tendency to pair up the d-electrons of a metal cation or atom to provide the necessary orbitals for hybridization. On the other hand, weak ligands do not have a tendency to pair up the d-electrons.
6. The d orbital used in hybridization may be either inner (n-1) d-orbitals or outer n d-orbitals. The complex formed by inner (n-1) d-orbitals, is called inner orbital complex whereas the complex formed by outer d-orbital is called outer orbital complex.
7. If unpaired electrons are present within the complex, then complex is paramagnetic in nature while if all the electrons are paired then complex is diamagnetic in nature.
Hybridization and Geometry of Complexes
Coordination Number
Types of Hybridizations Geometry Examples2
sp
Linear
[Ag(NH3)2]+
3
sp2
Triangular planar
[HgI3]-
4
sp3
Tetrahedral
[CoCl4]2-
4
sp2d
Square planar
[Ni(CN)4]2-
4
sd3
Tetrahedral
MnO4-, CrO42-
5
dsp3
Trigonal bipyramidalFe(CO)5
5
dsp3
Square pyramidal
[Ni(CN)5]3-
6
d2sp3
Octahedral
[Fe(CN)6] 4-
6 sp3d2 Octahedral[Fe(F)6] 3-
Examples of Octahedral complexes
(a) Inner Orbital Complexes:
[Co(CN)6]3- ion:
- In this complex, the oxidation state of cobalt is +3.
- The valence shell electronic configuration of Co3+ is 3d6.
- The CN- ligands are strong and therefore cause pairing of 3d-electrons.
- All six 3d-electrons are therefore paired and occupy three of the five 3d orbitals.
- The vacant 3d- orbitals combine with the vacant 4s and 4p orbitals to form six d2sp3-hybrid orbitals.
- These six hybrid orbitals overlap with six filled orbitals of ligands to form six-coordinate covalent bonds.

(b) Outer Orbital Complexes:
[Fe(F)6]3- ion:
- In this complex, the oxidation state of Iron(Fe) is +3.
- The valence shell electronic configuration of Fe3+ is 3d5.
- The F- ligands are weak and therefore cause no pairing of 3d-electrons.
- All five 3d-electrons are therefore occupied on five 3d orbitals.
- The vacant 4s- orbitals combine with the vacant 4p and two vacant 5d orbitals mixed with each other to form six sp3d2-hybrid orbitals.
- These six hybrid orbitals overlap with six filled orbitals of ligands to form six-coordinate covalent bonds.

Examples of tetrahedral complexes
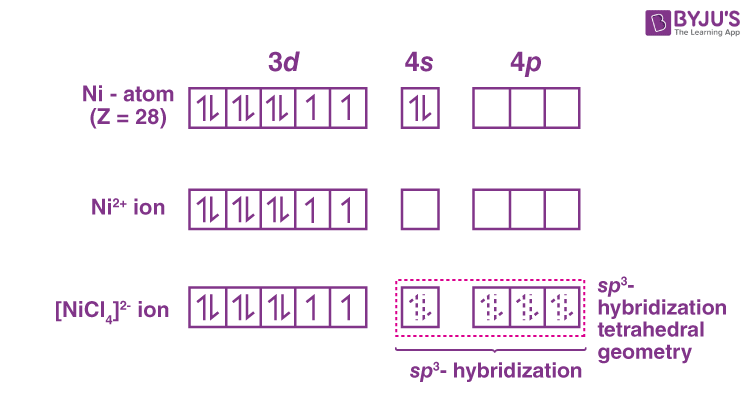
[NiCl4]2- ion:
- In this complex ion, the oxidation state of Ni is +2.
- The valence shell electronic configuration is 3d8.
- Since Cl- is a weak ligand, therefore no pairing of electrons will occur in 3d-orbitals.
- None of the five 3d- orbitals is vacant.
- Vacant 4s and 4p orbitals combine to give four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
- These four hybrid orbitals form bonds with four ligands by sharing four pairs of electrons.
[Ni(CN)4]2- ion:
- In this complex ion, the oxidation state of Ni is +2.
- The valence shell electronic configuration is 3d8.
- Since CN- is a strong ligand, therefore these ligands cause to pair up the two unpaired electrons in one d-orbital resulting in a vacant 3d-orbital.
- This vacant 3d-orbital gets hybridised with the vacant 4s and two 4p orbitals to give four dsp2 hybrid orbitals.
- These four hybrid orbitals form bonds with four ligands by sharing four pairs of electrons.
Limitations of Valence Bond Theory
- It could not explain the nature of ligands.
- It could not explain why the pairing of electrons occurs in the presence of strong ligands.
- It could not explain the colour and electronic spectra of complexes.
- It could not explain reaction rates and the mechanism of reactions of complexes.
- This theory does not provide any quantitative interpretation data about the thermodynamic and kinetic stability of coordination complexes.
Link nội dung: https://career.edu.vn/vbt-cn-8-a43075.html